Compiled and edited from History.com
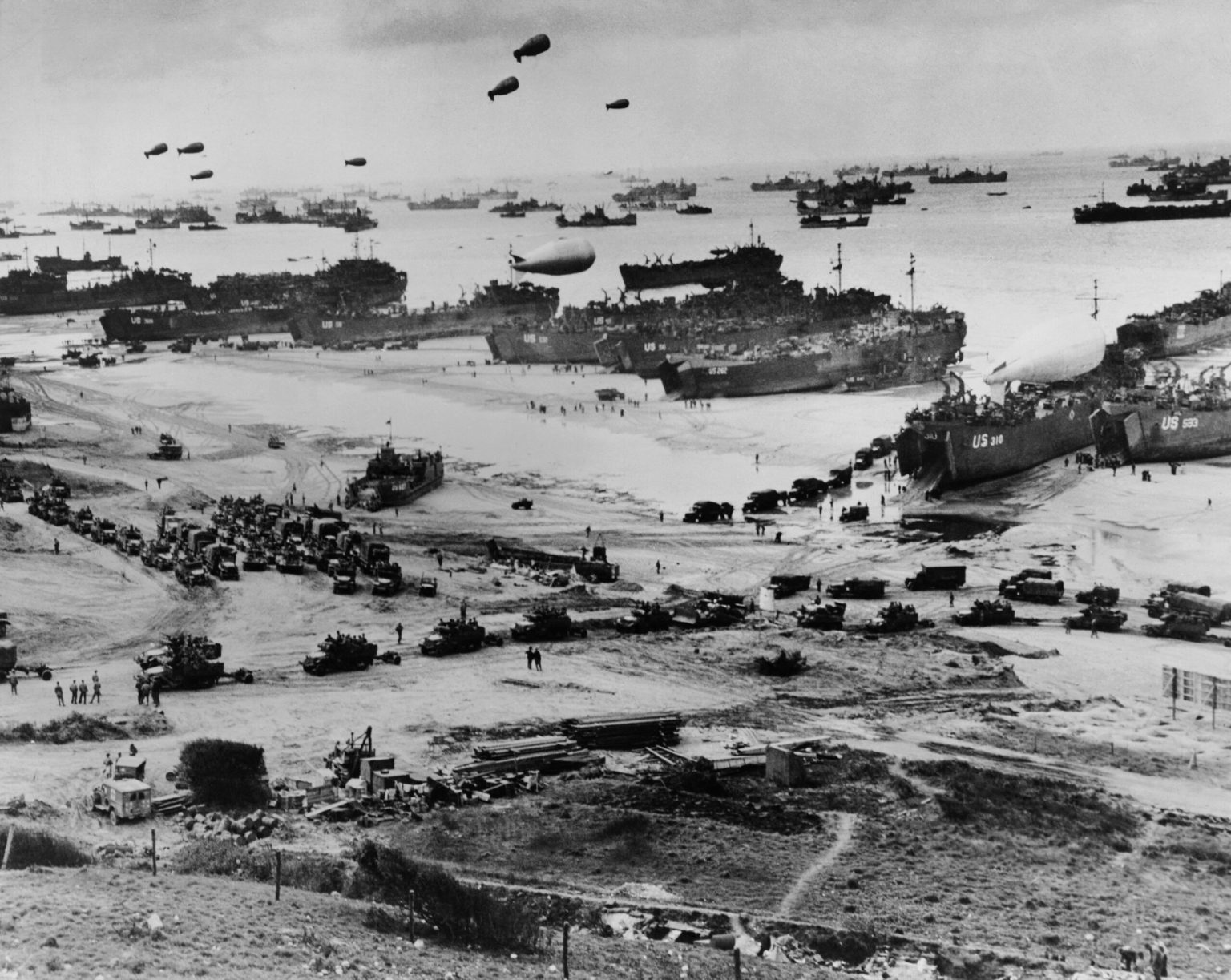
It was the largest amphibious invasion in the history of warfare. On June 6, 1944, more than 150,000 brave young soldiers from the United States, the United Kingdom and Canada stormed the beaches of Normandy, France in a bold strategy to push the Nazis out of Western Europe and turn the tide of the war for good.
By daybreak, 18,000 British and American parachutists were already on the ground. An additional 13,000 aircraft were mobilized to provide air cover and support for the invasion. At 6:30 a.m., American troops came ashore at Utah and Omaha beaches.
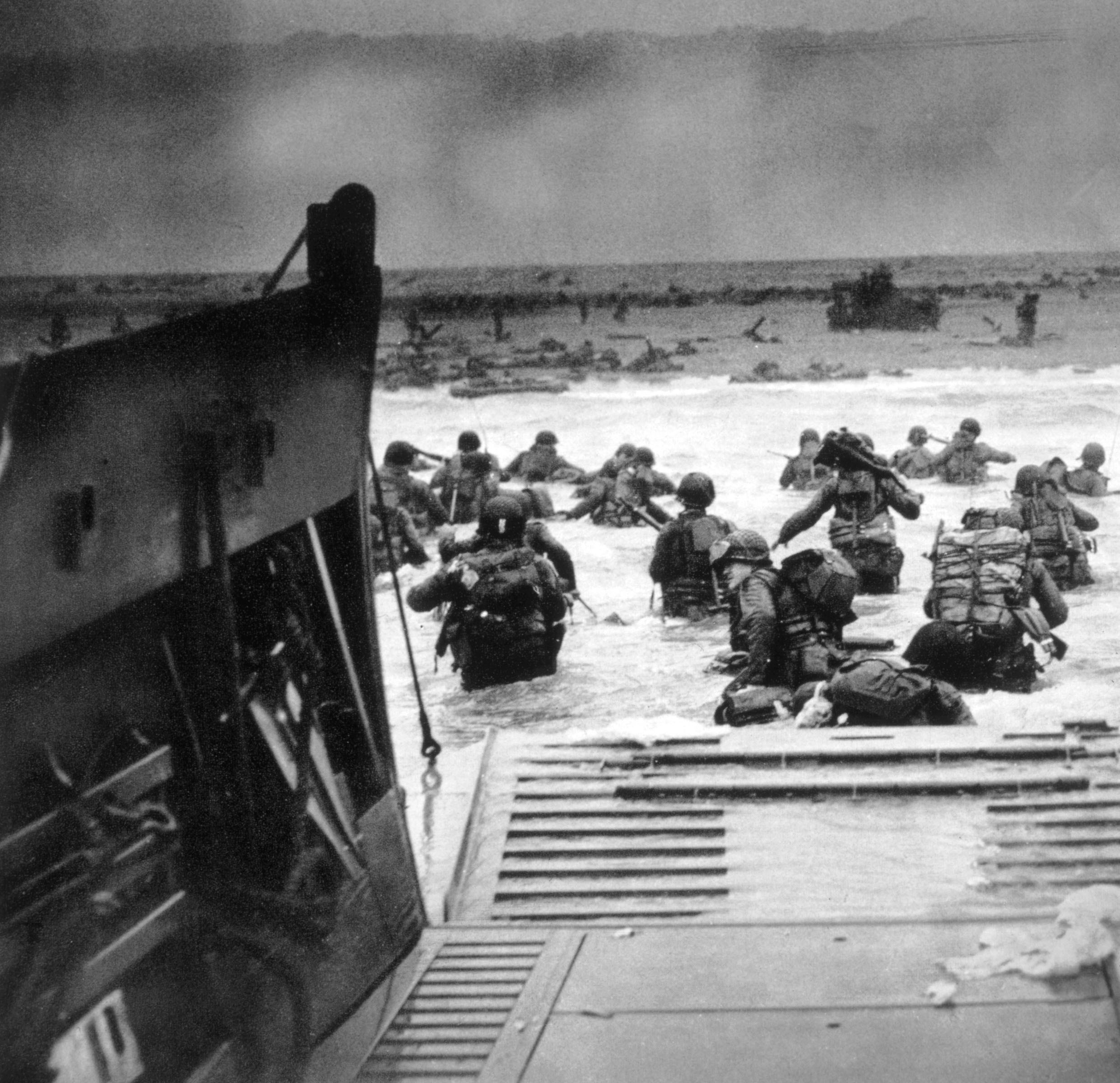
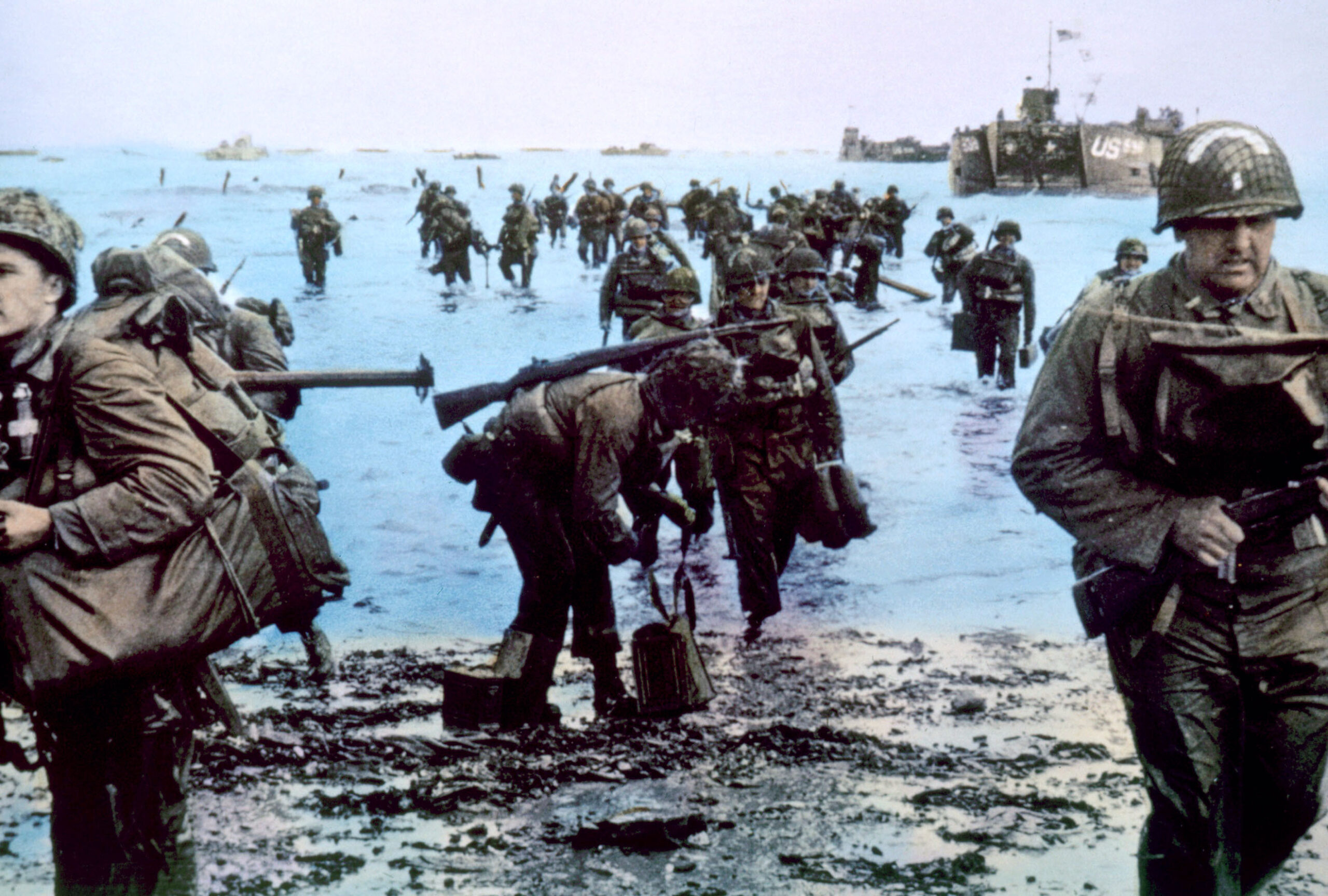
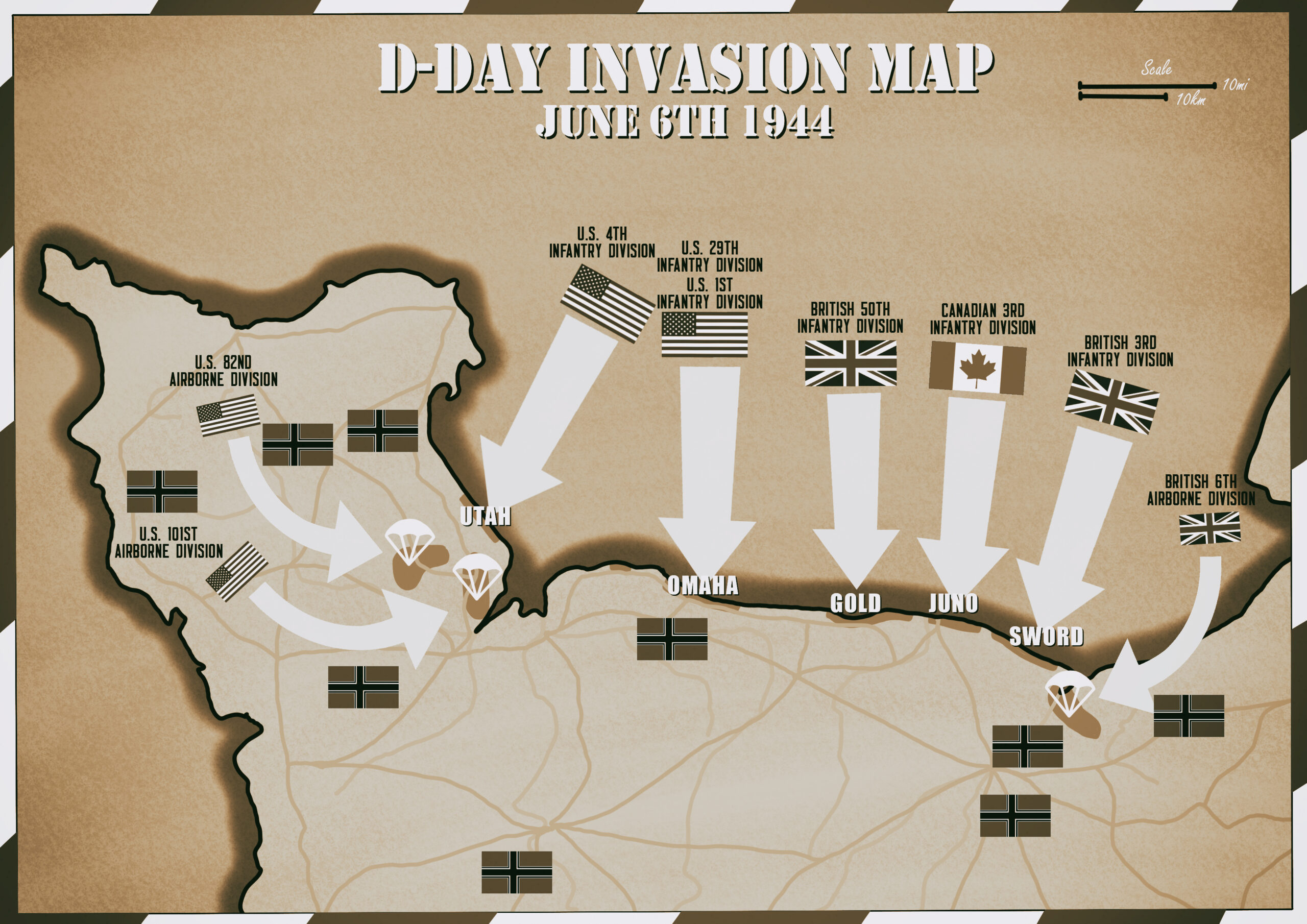



Because of bad weather and fierce German resistance, the D-Day beach landings were chaotic and bloody, with the first waves of landing forces suffering terrible losses, particularly the U.S. troops at Omaha beach and the Canadian divisions at Juno beach. But thanks to raw perseverance and grit, the Allies overcame those grave initial setbacks and took all five Normandy beaches by nightfall on June 6.
By day’s end, 155,000 Allied troops–Americans, British and Canadians–had successfully stormed Normandy’s beaches and were then able to push inland. Within three months, the northern part of France would be freed and the invasion force would be preparing to enter Germany, where they would meet up with Soviet forces moving in from the east.
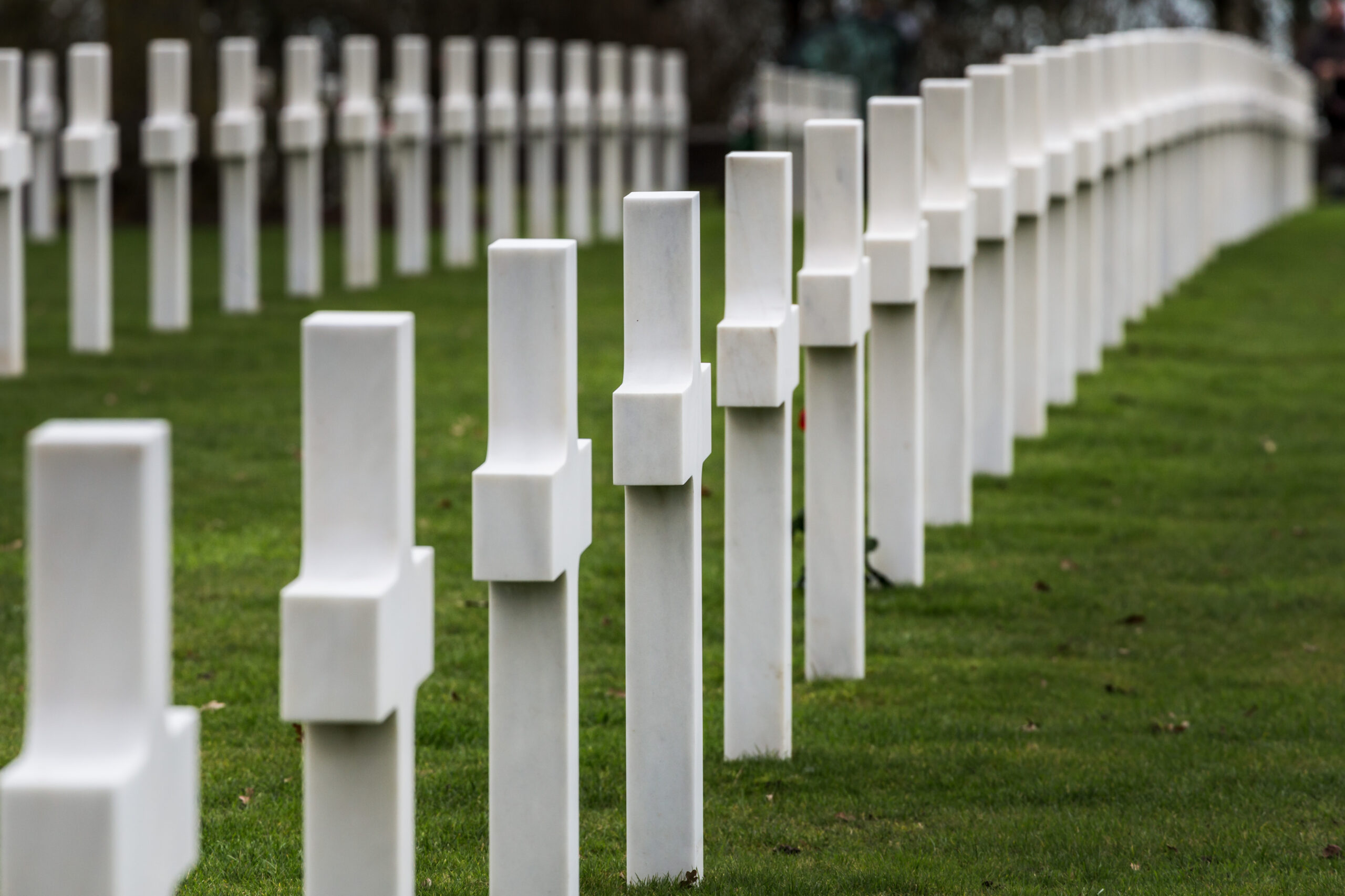
Allied casualties have been estimated as being between 4,000 and 5,000 men. German casualties on D-Day, meanwhile, have been estimated to be between 4,000 and 9,000 killed, wounded or missing. The Allies also captured some 200,000 German prisoners of war.








